Rise of Aqua-Culture in India
Rise of Aqua-Culture in India
November 18, 2022
Where do you think most of the fish we eat come from? The Ocean. Wrong. Rivers and lakes? Wrong again. It’s from Fish farms. Fish and fish products have been emerged as the largest group in agricultural exports in India, with 10.5 lakh tonnes in terms of quantity and 33,442 crores in value. More than 50 different types of fish and shellfish products are exported to 75 countries around the world. This accounts for around 10% of the total exports of the country and nearly 20% of the agricultural exports. Indian Fisheries and aquaculture is an important sector of food production, providing nutritional
| Global position | 3rd in Fisheries, 2nd in Aquaculture |
| Contribution to the Global Fish production | 6.3% |
| Contribution of Fisheries to GDP (%) | 1.1 |
| Contribution to Agricultural GDP (%) | 5.15 |
| Per capita fish availability (Kg) | 9.0 |
| The total fish production | 10.1 million |
| Annual Export earnings (Rs. In Crore) | 33,441.61 |
| Employment in sector (million) | 14.0 |
In budget of 2018-2019, Former Finance Minister, Arun Jaitley extending the facility of Kisan Credit Card to farmers engaged in fisheries, aquaculture and animal husbandry, has allocated a dedicated fund of Rs. 10,000 crore to develop the sector. Fish production also contributes around 1% to India’s gross domestic product and over 5% to the agricultural GDP. Aquaculture resources in India include 2.36 million ha of ponds and tanks, 0.798 million ha of flood plain lakes plus in addition 195 210km of rivers and canals, 2.907 million ha of reservoirs and that could be utilized
AQUA-CULTURE PRACTICES
In India, Two types of aquaculture are practiced. These are Fresh water aquaculture and brackish water aquaculture. Freshwater aquaculture involves the breeding of freshwater fish like carp, catla, rohu, magur, freshwater prawn, freshwater pearl culture and ornamental fish farming. Catla is grown in tanks and reservoirs in Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Brackish water aquaculture involves breeding of fish that habitat the sea like sea bass, grey mullet, tiger shrimp and mud crabs. It is practiced in States like West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala and Goa. Fish farmers use a mixture of oil cakes, rice bran, locally available snail, clam or mussel meat and buffalo meat to feed the fish.
This mixture may be blended with tapioca paste to form small balls that are then placed in pottery bowls at marked feeding sites. The water in which fish are farmed is important for the development of a good harvest.
The farmer should monitor the level of water hardness, acidity/ alkalinity, contaminants, industrial chemicals and pesticides in the water. He should also see that there is enough dissolved oxygen in the water for the survival of aquatic life. Common chemicals used in aquaculture are EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetate) disodium salt for removing water hardness, sodium nitrate for algae formation, ammonium chloride for boosting water fertility and formaldehyde, a bactericide.
Aquaculture in India
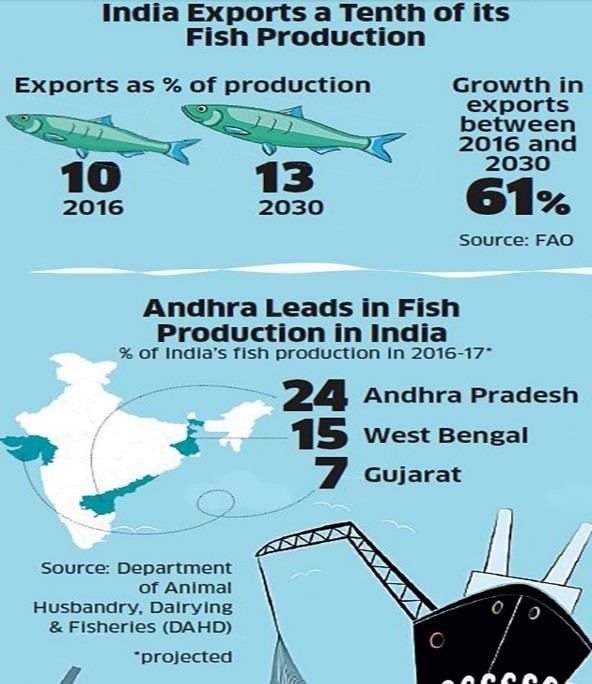
Andhra Pradesh ranks first in coastal aquaculture and fresh water aquaculture. It ranks second in fresh water fish production and overall value of fish/prawn production. Andhra Pradesh contributes nearly 40 per cent of the total marine exports of the country. Inland resources comprise 102 reservoirs of which 7 are large, 26 are medium and 69 are small reservoirs. There are two lakes – Kolleru Lake, a freshwater lake and Pulicat lake – a brackish water lake. 74,000 perennial, seasonal and long seasonal tanks, fishponds and freshwater prawn ponds for aquaculture are also present in Andhra Pradesh. Brackish water resources comprise 0.78 lakh hectares for shrimp culture, a coastline of 974 kms and 508 fishing villages.
Chhattisgarh has around 1.549 lakh hectares of water available for aquaculture in the form of river, reservoirs, ponds and tanks. The State also has two major river systems – Mahanadi and Godawari and their tributaries that form a network of 3573 kms. Fishing in rivers is free for members of scheduled tribes and scheduled castes. The C.G. Rajya Matsya Mahasangh has 6 fish seed hatcheries with a total water area of 60 hectares. These Centres produce 30-35 crores spawn and 4.5 crores fry annually. Two fish hatcheries at Demar (25 hectares.) and Salud (10 hectares) have been established with assistance from the World Bank (External website that opens in a new window).
In West Bengal, fishing harbours at Sonarpur and Frasergunge provide facilities to sea-going fishermen. Training Centres in all the districts provide training to the fishermen, youth, women, in service officers and college students. The government fish farms at Juneput (East Midnapore), Kalyani (Nadia) and Barasagardighi (Malda) are involved in producing fish-seed and table fish which is supplied to local fish farmers at a government price.
Haryana – The main sources for capture fisheries in the State are its rivers, lakes and dams. It is reported that 55 species of fish are available in these natural water bodies. Haryana stands second (External website that opens in a new window) in the average annual fish production per unit area in the country. The average annual fish production in the State is 4209 kgs.
Himachal Pradesh – In this state, aquaculture is mostly practiced in the Gobind Sagar and Pong Reservoirs. Many people visit this State for the adventure sports of angling and game fishing. Types of fish available here include the brown trout, rainbow trout, golden mahseer and carp.
Trial Reports- Calcomag demo in Vannamei
Aquaculture production has grown enormously in recent years and Penaeid shrimps are one of the most important cultured species worldwide, especially in Asia, due to their high economic value and export.
Introduction of exotic ‘vannamei’ shrimp into India’s coastal aquaculture system has significantly contributed to maintaining the momentum in the country’s marine product exports. According to MPEDA, Indian marine product exports are doing quite well over the last few years. Major factor that contributed to the increase in exports was the introduction of vannamei shrimp variety into our coastal aquaculture systems.
Indian marine products are principally supported by frozen shrimp, which is mainly sourced from the coastal aquaculture farms. India farms mainly two varieties of shrimp — ‘Pacific White Leg Shrimp’ (Litopenaeus vannamei) and ’Indian Black Tiger Shrimp’ (Penaeus monodon).
Advantage of P. vannamei
- Penaeus vannamei has the potential to grow as fast as P. monodon (at up to 3 g/wk) up to 20 g under intensive culture conditions.
- They are amenable to culture at very high stocking densities of up to 150/m2 in pond culture, and even as high as 400/m2 in controlled recirculated tank culture
- Tolerates a wide range of salinities, from 0.5-45 ppt, is comfortable at 7- 34 ppt, but grows particularly well at low salinities of around 10-15 ppt.
- P. vannamei is very tolerant to low temperatures (down to 15°C) enabling them to be cultured in the cold season.
- P. vannamei require lower protein feed (20-35%) than P. monodon resulting in a reduction in operational costs and amenability for closed, heterotrophic systems and has a better Food Conversion Ratios (FCRs) of 1.2.
- Specific Pathogen Free (SPF) brood stocks are available for this species to produce disease free larvae.
| Farmer name | M.lakshman rao garu |
| Name of the village | Kothapallem |
| Mandal | Nagayalanka |
| District | Krishna district |
| Mobile number | 9440277237 |
| Demo Product | Aries Calcomag |
| Recommended dose | 10 kgs/1 acres |
| Date & time | 10-12-2015 & 10:30 a.m. |




Conclusion – CSS Team
- There is an increase in 3 gm weight in 20 days
- Good Pond colour
- Better Plankton development
- Quality improvement of water.