Soil-Where life begins
Soil-Where life begins
November 18, 2022
World Soil Day
In 2002, The International union of Soil Sciences adopted a resolution proposing the 5th December as World Soil Day to celebrate the importance of soil as a critical component of the natural system and as a Vital contributor to human wellbeing. The theme for World Soil Day 2017, as dedicated by the Global Soil Partnership, was “Caring for the Planet starts from the Ground”.
World soil day 2018 theme was #StopSoilPollution. As soil pollution is often neglected or overlooked. There are many changes we have made to our planet, some of its impacts are virtually invisible, and soil pollution is a good example. Thus Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) came up with this campaign “Be the solution to Soil Pollution” for World Soil Day, 2018.
Soil, Soil can be commonly defined as a mixture of small rock particles/debris and organic materials/ humus which develop on the earth surface and support the growth of plants. In India, Soil has been classified from an ancient period even though it was not as detail as the modern classifications. In the Modern Period, when people started to know about various characteristics of soil they begin to classify soil on the basis of texture, color, moisture etc.
Soil is a dynamic entity where complex interactions among its biological, chemical and physical componenets take place. Soil directly and indirectly affect agricultural productivity, water quality, and the global climate through its function as a medium for plant growth, and as a regulator of water flow and nutrient cycling. The soil structure should be suitable for the germination of the seeds and the growth of the roots, and must have characterstics that enhance the storage and supply of water, nutrients, gases and heat to the crop.
Soil Properties
- Soil Physical porperties determine many key soil processes and thus the agronomical potential of a
- Soil texture is a description of the size distribution of the mineral soil
- Soil structure describes the arrangement of mineral particles and organic matter in the soil and particularly the arrangement of pores among these particles. Organic matter plays an important role in facilitating aggregate formation and its long term decline contribute to the loss of soil structural
- Soil permability is a broad term used to define the ability of the soil for transmitting water, and it must be known for accurate management of
- Soil host a complex web of organisms which can influence soil evolution and specific soil physical and chemical
- Soil organic matter is a key factor affecting biological activity in soils. It is the carbon source for organisms, including soil microbiota. Not only the amount, but also the type of organic compounds in the soil determines its biological activitity; e.g., microbial activity is greatly increased by incorporating fresh organic residues (such as green manure or crop residues), which can be readily mineralized by
Types Of Soil
- Alluvial soil [43%]
- Red soil [18.5%]
- Black / regur soil [15%]
- Arid / desert soil
- Laterite soil

Alluvial soil
- Highly fertile. Widespread in northern plains and river
- Humus, lime and organic matters are present.
- Rich in: potash.
- Poor in: phosphorous.
- Wheat, rice, maize, sugarcane, pulses, oilseed etc are cultivated mainly.
Red soil
- Seen mainly in low rainfall
- Absence of lime, kankar (impure calcium carbonate).
- Deficient in: lime, phosphate, manganese, nitrogen, humus and
- Wheat, cotton, pulses, tobacco, oilseeds, potato etc. are cultivated.


Black soil / regur soil
- Regur means cotton – best soil for cotton cultivation.
- High water retaining
- Rich in: Iron, lime, calcium, potassium, aluminum and magnesium.
- Deficient in: Nitrogen, Phosphorous and organic
Laterite soil
- Name from Latin word ‘Later’ which means Brick.
- Rich in: Iron and Aluminum
- Deficient in:Nitrogen, Potash, Potassium, Lime, Humus
- Rice, Ragi, Sugarcane and Cashew nuts are cultivated mainly.


Desert / arid soil
- Seen under Arid and Semi-Arid conditions.
- High salt
- Lack of moisture and
- Nitrogen is insufficient and Phosphate is
Soil is one without a doubt of the most significant parts of the ecosystem, contributing to our food, water and energy and playing an important part in reducing the impact of climate change. Thus, Soil health is crucial & Concern for soil health of their own farm holding by farming community can never be undermined. Therefore, Farmer has always been doing one exercise or other to sustain its productivity through external application of farm wastes, green manuring and chemical nutrients to supply the required nutrients to the crops. However, with ever increasing demand for increasing the productivity per unit area and narrowing cost benefit ratio has made farmer more sensitive to the soil fertility status and there by fertilizer management and soil health.
The Agriculture scientific community in India is constantly making effort to have farmer friendly Soil Testing Kit. A Soil scientist at ANGRAU, Hyderabad has come up with low cost soil test kit that can analyze about 25 samples. This newly innovated soil test kit is enabling the farmer himself to do the analysis at field level and apply fertilizer as per soil test values. This Soil Test Kit has been formulated and fabricated in such a simple mode so that even an ordinary illiterate farmer can also test his soil of his field at village level. He can very easily diagnose the organic carbon, pH, available nitrogen, phosphorus, potash & Sulphur of his soil and match with it the color charts of the kit and go for recommended doses of nutrients, fertilizers and decide the quantity to be applied. The results obtained here are only qualitative in nature to have firsthand insight into nutrient status of soils of farm holdings
Methods of Soil Analysis Using Soil Test Kit
- pH (Soil Reaction):
- C. (Organic Carbon):
- Available Nitrogen:
- P2O5 Available Phosphorus:
- K2O Available Potassium:
- SO4 Available Sulphur:
- Calcareousness of Soil:
- Available Zinc of soil:
- Available Iron of soil: 10.Available Boron of soil:
Interpretation of Results
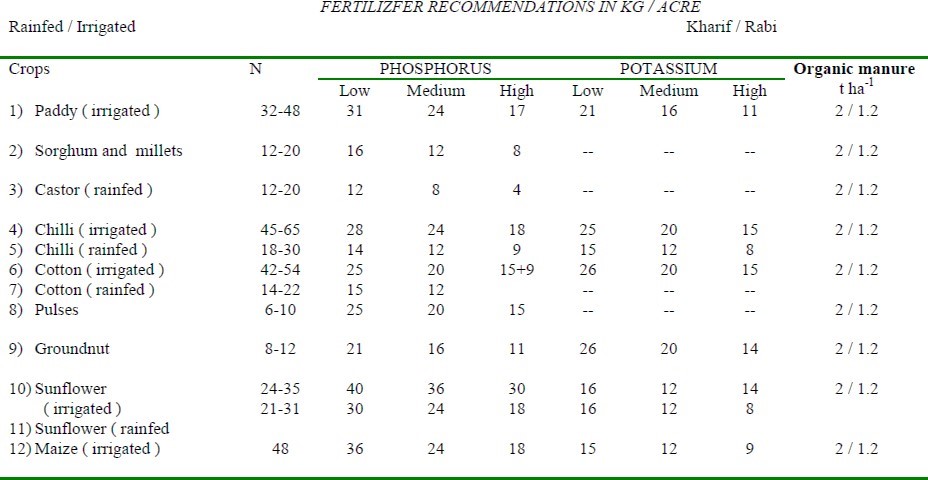
After knowing the fertility status from all soil parameters of each representative soil fertilizer recommendations may be given as per the ready reckoners.
Evaluation of Portable Soil Testing Kit
Results of fertility status carried by using reagents in portable soil test kit are compared with quantitative analysis. Its efficiency was calculated for each parameter comparing with quantitative analysis and its overall efficiency is presented. The efficiency of portable soil testing kit developed at ANGRAU was found to be efficient with 84% in all parameters put together compared to quantitative methodologies in the laboratory involving sophisticated instrumentation techniques. Further, it was found that it is helpful to farmers to test their farm holdings themselves on spot and take up fertilizer recommendations to different crops without much waiting for laboratory report. Hence, it is farmers friendly most useful for the Indian farmer at affordable price to know the fertility status immediately. The Portable Soil Testing Kit developed at ANGR Agricultural University, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad has been widely accepted by the farming community since 2005. Aries Agro Limited has been associated and using this kit since 2013